Before we get to flushing your DNS cache, we need to break down a couple of concepts.
What is a DNS Cache?
When you access a website, your computer needs to find the IP address of that website to connect to it. The DNS server is responsible for providing this information, and the DNS cache is a localized temporary storage area where this information is stored on your computer.
DNS cache stores the results of recent DNS lookups for a certain period of time, so that when you try to access the same website again, your computer can use the saved information instead of requesting it from the DNS server again. This results in faster response times and improved performance when browsing the web.
DNS cache is a mechanism that helps to speed up the process of accessing websites by storing the IP address information of recently accessed websites on your computer for a certain period of time.
Why flush DNS Cache?
There are a few reasons why you might need to flush your DNS cache. Here are a few examples:
- You are experiencing problems with a website.
- You need to update your DNS settings.
- You are troubleshooting a network problem.
- You want to clear your browsing history.
If you are experiencing problems with a website, flushing your DNS cache can help to resolve the issue. This is because the DNS cache may be storing outdated information about the website. Flushing the cache will force your computer to retrieve the latest information from the DNS server.
If you need to update your DNS settings, you will need to flush your DNS cache in order for the changes to take effect. This is because the DNS cache stores a copy of your current DNS settings. Flushing the cache will clear the old settings and allow your computer to use the new settings.
If you are troubleshooting a network problem, flushing your DNS cache can help to narrow down the cause of the problem. This is because the DNS cache can sometimes store incorrect information about network resources. Flushing the cache will clear the old information and allow your computer to retrieve the latest information from the DNS server.
If you want to clear your browsing history, you will need to flush your DNS cache. This is because the DNS cache stores a record of all the websites you have visited. Flushing the cache will clear this record, which can help to protect your privacy.
How to flush DNS Cache in Ubuntu?
To flush the DNS cache in Ubuntu 22.04, you can use the following steps:
- Open a terminal window.
- Type the following command and press Enter:
$resolvectl statistics
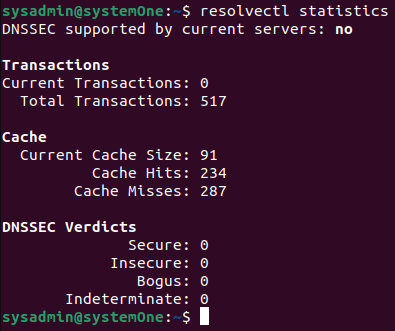
- The output of this command should show that the “Current Cache Size” is 0.
- Now you can run the following:
$resolvectl flush-caches
You can run the “statistics” command again to confirm the successful flushing of the cache.
Note: In Ubuntu 22.04, systemd-resolved was renamed to resolvectl. resolvectl is a more powerful and flexible DNS resolver than systemd-resolved.How Often Should You Flush Your DNS Cache?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question. It depends on how often you use your computer and how often you visit websites. If you experience problems with a website on a regular basis, you may want to flush your DNS cache more often.
Is Flushing DNS Cache Safe?
Yes, flushing your DNS cache is safe. It will not damage your computer or your data. However, it will clear your browsing history, so you may want to back up your bookmarks or other important information before you flush your cache.
Conclusion
Flushing your DNS cache is a simple way to fix problems with websites and to troubleshoot network issues. It is a safe and effective way to clear your browsing history and to update your DNS settings.
