How to Change Sleep Settings in Ubuntu 22.04
Saving power is another reason why computers include a “sleep” mode for when they are not in use. When a computer enters sleep mode, it stops doing everything that isn’t essential. After a certain length of time with no input from the user, most computers and other electronic devices enter sleep mode.
Most laptops enter a sleep state when the lid is closed. A computer may be woken up from hibernation by touching a key, clicking the mouse, or pushing the power button. Almost every part of your computer powers down when you put it into standby or sleep mode.
Everything from your central processing unit and hard drive to your network interface cards and, in most cases, everything else is included. One notable exception is RAM (memory), which must be preserved for a speedy restart.
Due to the irretrievable nature of RAM data when a computer is powered off, this feature must remain active. A computer’s RAM may be damaged if it went to sleep for too long, although I’ve never heard of such a thing happening in practice.
If you need to save energy or are too cautious, you may utilize hibernate. This saves the contents of your RAM to your hard drive so you may access them offline. That’s only a transitional state between awake consciousness and total shut down.
Instead of keeping your RAM turned on, your computer saves it to the hard drive so it can recall your last actions. Although it does not work perfectly on all systems and takes a bit longer to enter and leave hibernation than sleep would, it is typically quite excellent (like with sleep).
The following are the steps you need to take to effectively modify Ubuntu’s 22.04 sleep settings:
Method 1: Use Power Settings
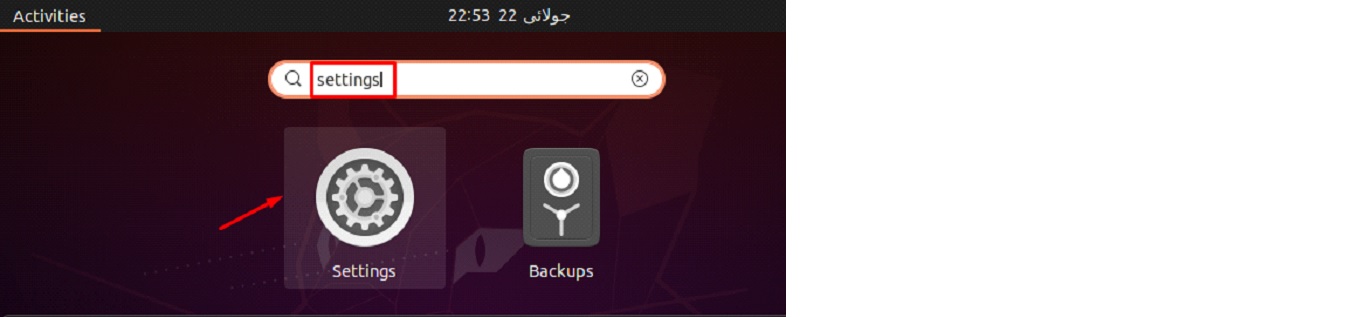
Step 1: Starting at the Activities Overview, type ‘settings’ into the search field, and then select the Settings button that appears.
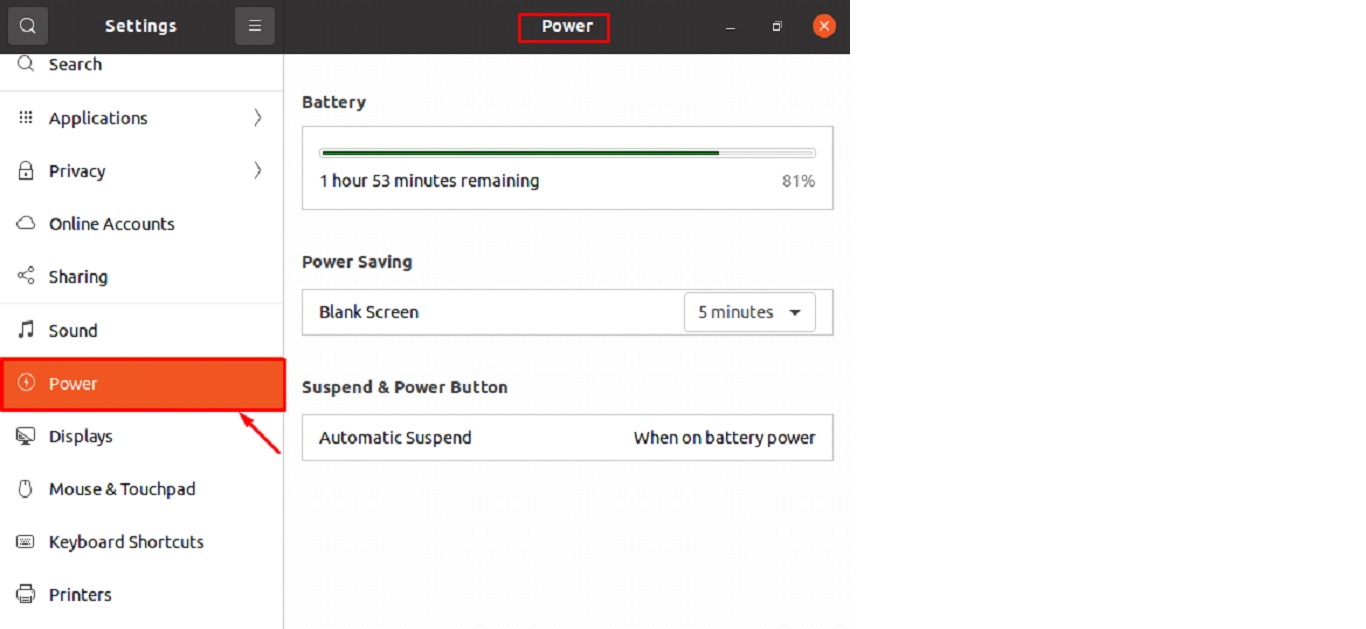
Step 2: Once you’ve opened the Settings window, choose “Power” from the left sidebar to see the Power panel.
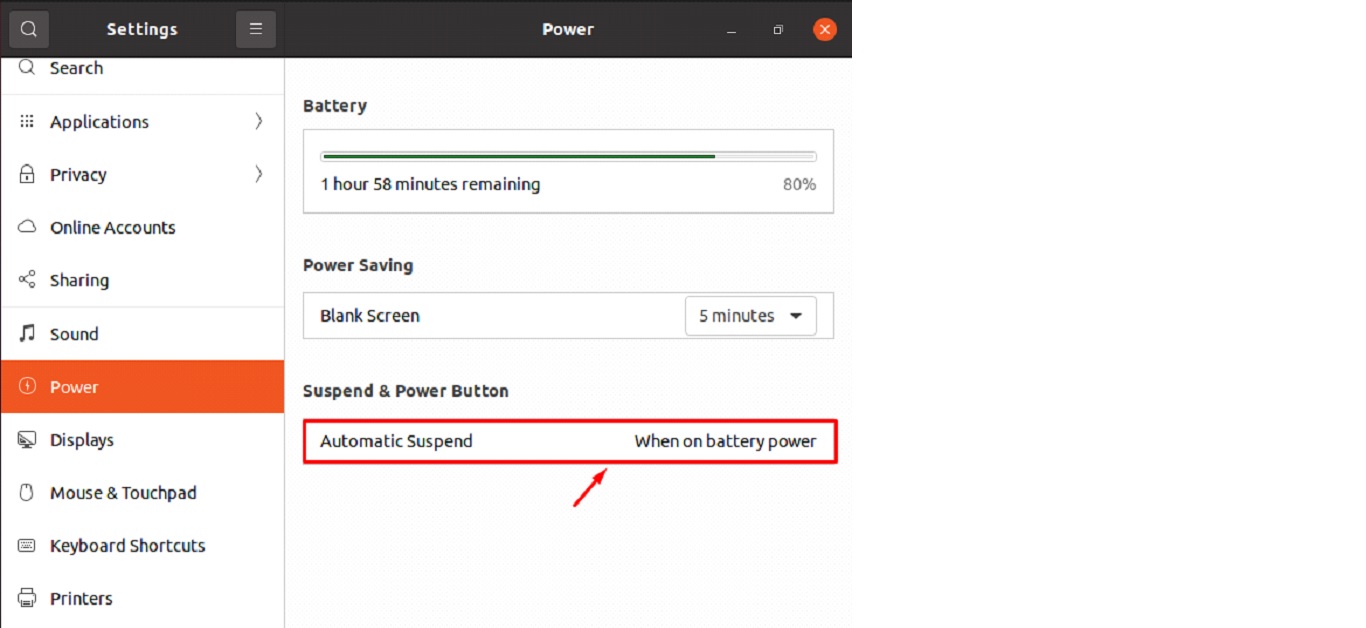
Step 3: From the “Suspend & Power Button” option, choose Automatic Suspend.
Step 4: After activating the switch, selecting “Plugged In” or “On Battery Power,” and deciding on a delay period, the device will begin functioning.
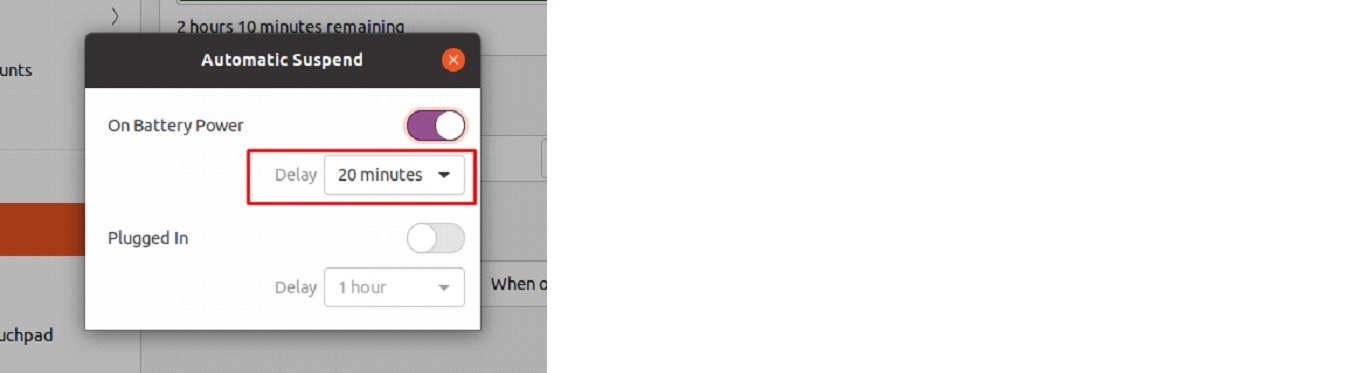
You need to select “On Battery Power” and programmed a delay of 20 minutes. Your preferences may be modified to suit your needs. What this means is that after 20 minutes of inactivity, your laptop will turn off automatically if it is using battery power.
Method 2: Use Terminal
If you want to put your Ubuntu computer to sleep or hibernate, you can’t do so directly from the terminal, but there are a few ways to do so:
To put your computer to sleep, open the terminal and type:
$ systemctl suspend
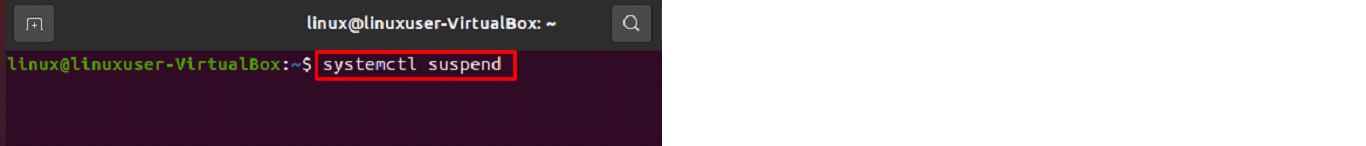
After entering this command, your computer will automatically shut down and display a black screen. To initiate hibernation on your computer, use the command shown below:
$ systemctl hibernate
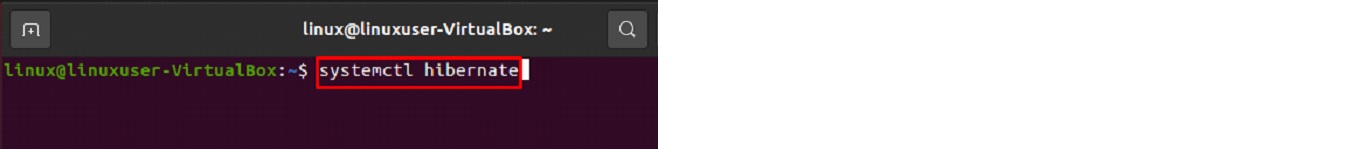
After entering this command, the screen will go black to signify that hibernation has been activated.
Conclusion
After a specified amount of inactivity, your computer will enter sleep mode. In this piece, we walked you through several easy ways to modify your Linux OS’s sleep parameters (Ubuntu). The first is through the terminal, and the second is through the power options. You may also customize your sleep routine by writing scripts.

