
How to Remove and Uninstall Samba from Debian 11
Samba is free software that permits users to share files and printers across different operating systems. But, if users wish to free up disk space or no longer need it, they can easily remove and uninstall it from the Debian 11 system. This will free up more disk space and reduce potential conflicts with other packages.
This guide will explain how to Remove and Uninstall Samba from Debian 11:
- Using apt Package Manager
- Using dpkg Package Manager
How to Remove and Uninstall Samba from Debian 11?
Before removing or uninstalling Samba from Debian 11, it is necessary that Samba is already installed in the system. Let us explore the step-by-step instructions to stop as well as remove or uninstall Samba from the system.
Prerequisite: Stop the Samba Service
First, users need to stop the Samba service from running. For instance, open a terminal and run the below command:
sudo systemctl stop smbd |
|---|

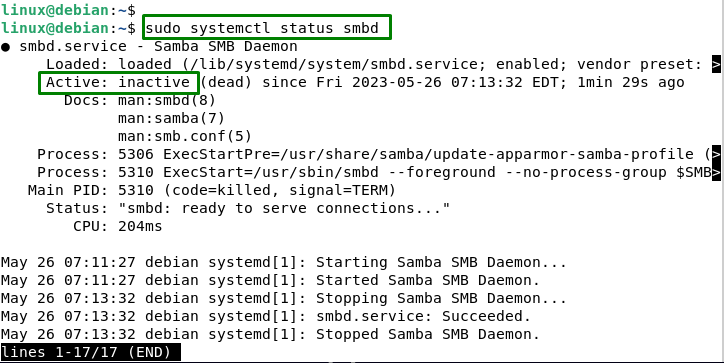
This stops the Samba from being executed in the background. Users can verify that by typing the below command:
sudo systemctl status smbd |
|---|
Method 1: Using apt Package Manager
Users need to remove the Samba packages from Debian 11. For this, follow the below procedure.
Remove Samba and its Dependencies
For uninstalling Samba and its dependencies that are not required, users can utilize the command below:
sudo apt autoremove samba |
|---|
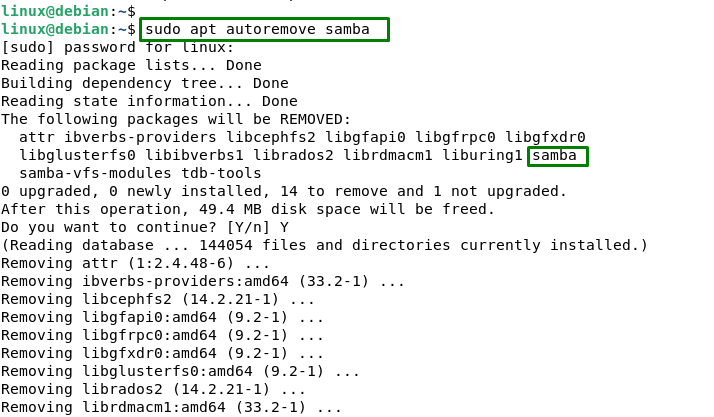
This command removes Samba and any packages that were installed as dependencies of Samba but are not required by any other packages on the system.
Remove Samba Configuration Files
For removing the Samba configuration files from Debian 11, execute the below script:
sudo apt purge samba |
|---|
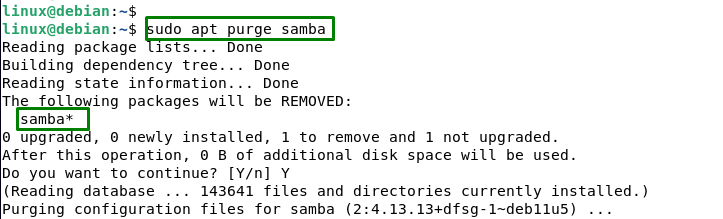
This command removes Samba and deletes its configuration files and data files from the system. It confirms no traces of samba were left on the system.
Remove Samba Completely
If users want to remove all content regarding Samba and all its dependencies from the system, utilize the below command:
sudo apt -y purge --autoremove samba |
|---|
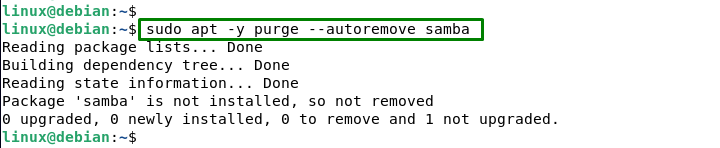
This command does the same as the previous two commands, but it also removes any packages that depend on Samba or were installed as dependencies of Samba.
Reboot the System
Finally, users need to reboot the operating system to save changes. To do that, type the below command:
sudo reboot |
|---|
![]()
This restarts the system and completes the removal and uninstallation of Samba from the Debian 11 system.
Method 2: Using dpkg Package Manager
Dpkg is a low-level package manager that does not automatically handle dependencies or configuration files. Let us explore the practical implementation for removing Samba from Debian 11 via dpkg.
List All the Installed Packages
To remove Samba, users need to first list all the installed packages that start with Samba. To do that, type the following command:
dpkg -l | grep samba |
|---|
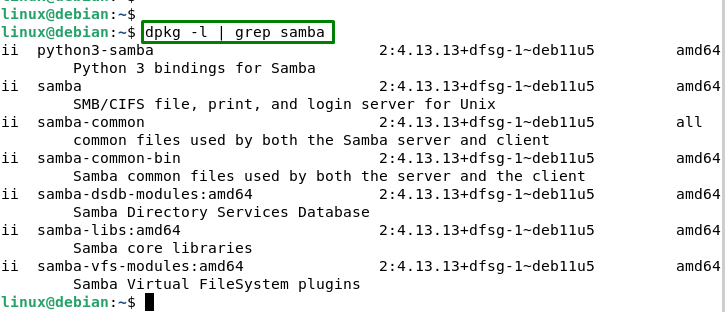
This lists all installed packages that contain samba in their name or description. If you see any output, it means that some Samba packages are still present in the system.
Remove Samba Package
Then, users need to remove each package individually using the following command:
sudo dpkg --purge samba |
|---|
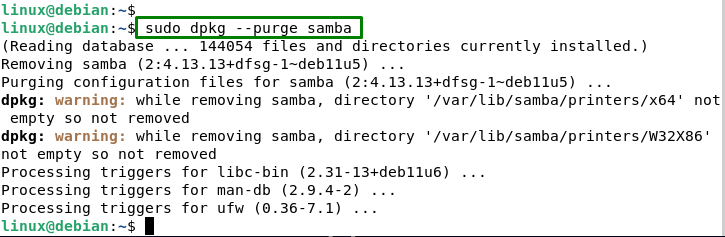
It removes the package as well as the files that are linked with it.
Note: Using dpkg may leave some dependencies or configuration files behind, so users may need to run “sudo apt autoremove” or “sudo apt autoclean” afterward to clean up the system.
Reboot the System
In the end, users are required to reboot the system to save changes. For instance, type the following command:
sudo reboot |
|---|
![]()
It restarts the system and completes the removal and uninstallation of Samba from the Debian 11 system.
Conclusion
To uninstall or remove Samba from the Debian 11 system, users can utilize the “apt” and “dpkg” package managers. These package managers enable users to remove all packages, dependencies as well as unused data. After that, users need to restart the system to complete the process. This will completely erase Samba and its configuration files from the system. Users should only do this if they no longer need samba or any of its features.

