
Time Command in Linux
The efficiency and effectiveness of any task or process are measured by the time parameter. A good processor with good processing speed is also judged over time.
In Linux, the time command is used to determine how long a command runs, and it prints a real-time summary.
And here is a guide to using the time command in Linux.
Syntax of time command
$ time [options] [command]
For example:
$ time sleep 2
Output:

In the above example, we created a dummy job that lasts 2 seconds.
Explanation:
real: the actual time that the computer’s processor executes the instruction
user: the time the command has been executed since the Enter key was pressed
sys: the amount of time the system or kernel takes to execute the command
Examples
1. -p: display the time in POSIX format
$ time -p sleep 2
Output:

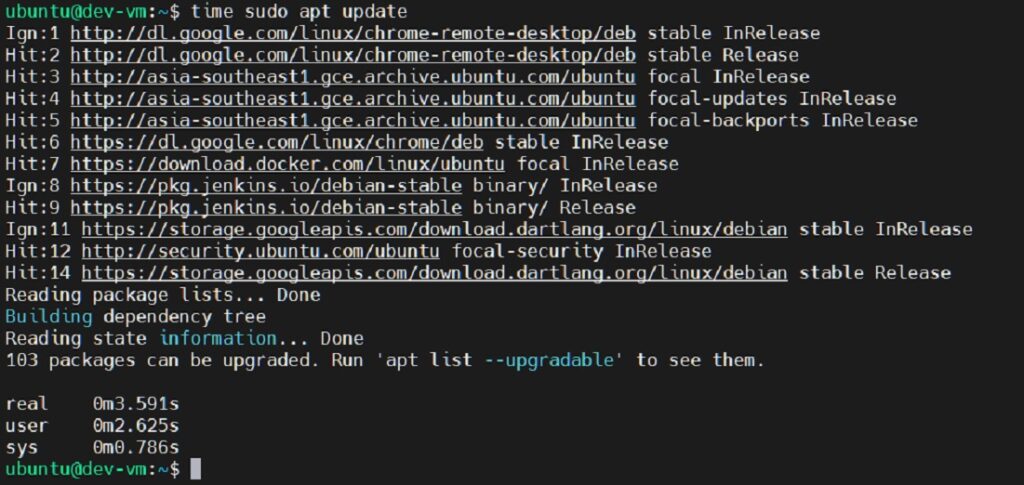
2. update the repository
$ time sudo apt update
Output:
Conclusion
Above is a tutorial on how to use the time command in Linux.
Thank you for reading.

